Jul 4th 2020
“THE WORST year in the history of aviation” is how the International Air Transport Association (IATA) describes 2020. The international airline-industry physique expects carriers’ revenues to fall by half and debt to swell by $120bn to $550bn. To reduce prices airways have grounded planes and put workers on unpaid go away.
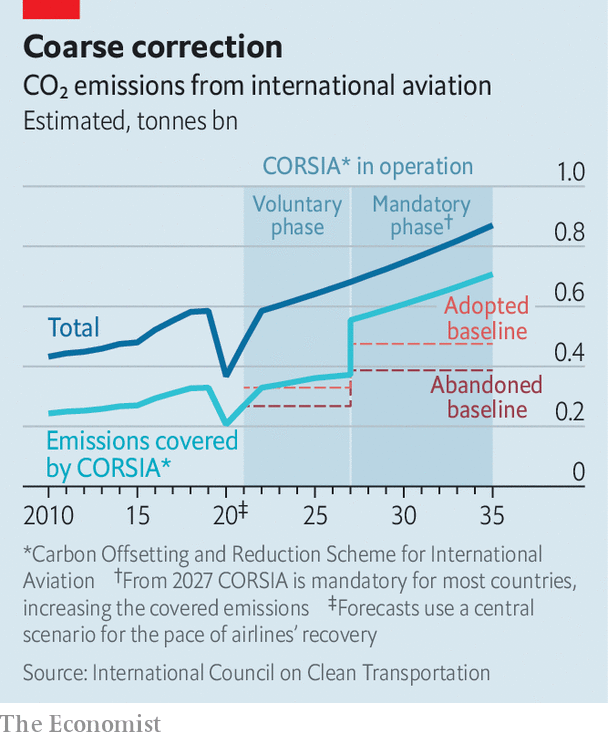
Another slashed expense is that of climate motion. Aviation emits 3% of artificial carbon dioxide. That share might rise to 5-9% by 2050, in response to the International Energy Agency, a forecaster. To curb these emissions, in 2013 the European Union tried so as to add worldwide aviation to its emissions-trading programme, together with flights connecting EU airports to these exterior the bloc. The {industry} cried foul. In a compromise the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), an company of the UN, devised the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation. CORSIA, as it’s recognized for quick, is because of begin subsequent yr. It compels airways to purchase offsets for any further CO2 produced by worldwide flights above a baseline.
That baseline has develop into hotly contested. It was initially set on the {industry}’s common emissions for 2019 and 2020. Now emissions are forecast to fall by 37% this yr, which might imply a decrease baseline—and so, in time, increased offsetting prices. So IATA proposed utilizing simply emissions from simply 2019 as an alternative. On June 30th ICAO’s 36-member council agreed, no less than for CORSIA’s first three years (see chart).
Environmental teams are up in arms. The scheme already lacked chunk, since it’s voluntary till 2027 and doesn’t embrace home flights, a few third of the {industry}’s emissions. Countries representing three-quarters of aviation’s carbon footprint have signed up however flights between these which have opted in and people which haven’t are excluded. Dan Rutherford of the International Council on Clean Transportation, an NGO, calculates that on pre-pandemic traits the unique plan would have lined solely 9% of aviation emissions from 2021 to 2035 (when the scheme is scheduled to finish).
In truth, the two-year common was expressly designed to account for low-emission years—a lesson realized from an early try to set the baseline in 2010, which was thwarted by the eruption of Eyjafjallajökull, an Icelandic volcano which grounded flights in Europe.
Another grievance is that most of the offsets airways should buy are ineffective. A report in November final yr by the NewClimate Institute and the Stockholm Environment Institute, two think-tanks, discovered that 80% of CORSIA’s potential offsets are unlikely to have any further profit to the climate. Since then ICAO has, to its credit score, restricted the provision of junk offsets within the scheme, although inexperienced campaigners say it has not gone far sufficient.
Offsets’ discount costs additionally counsel one thing is amiss. In 2018 the common worth within the “voluntary market” (exterior of mandated schemes) was $Three per tonne of CO2, a few sixth of the carbon worth within the EU emissions-trading scheme. Last yr EasyJet, a British low-cost provider, introduced plans to offset all its annual emissions. This will price it a footling $32m. New offest initiatives created in anticipation of CORSIA boosted provide, which is predicted to be 4 instances increased than demand.
Industry executives declare that the unique baseline would have imposed crippling prices. That appears overblown. Sparse protection and a budget offsets imply the fee to the {industry} is low. Assuming an offset worth of $5 per tonne of CO2, Mr Rutherford estimates the change within the baseline will save airways $350m a yr. That is lower than 1% of the forecast working cashflow in 2021 for a panel of 37 listed airways.
Forgoing these financial savings would have been a small worth to pay for burnishing airways’ reputations as they search billions in authorities bail-outs. Accusations of greenwashing will make calls to connect probably a lot costlier inexperienced strings to the rescue packages develop louder.

Be First to Comment